Hurricane Maria left nearly all people in Puerto Rico without power for months, some places never to have access again and others on a minimum of a five-year timeline before reconnecting to the grid. It also exposed an even deeper problem – the lack of renewable energy alternatives fueling the island with less than 1% of all power coming from renewable sources. A particularly troubling statistic considering Puerto Rico is a place that sees sun and wind all year round. A problem that manifested itself as people waited in 18-22 hour lines at gas stations for Diesel fuel for their generators, cars, and homes to reboot their energy essentials. And for those without generators, lack of power meant lack of refrigeration for necessities like insulin, a major contributor to the 3,000 casualties of Hurricane Maria. The only silver lining is that this tragedy has motivated new renewable energy legislation in Puerto Rico announced this week.
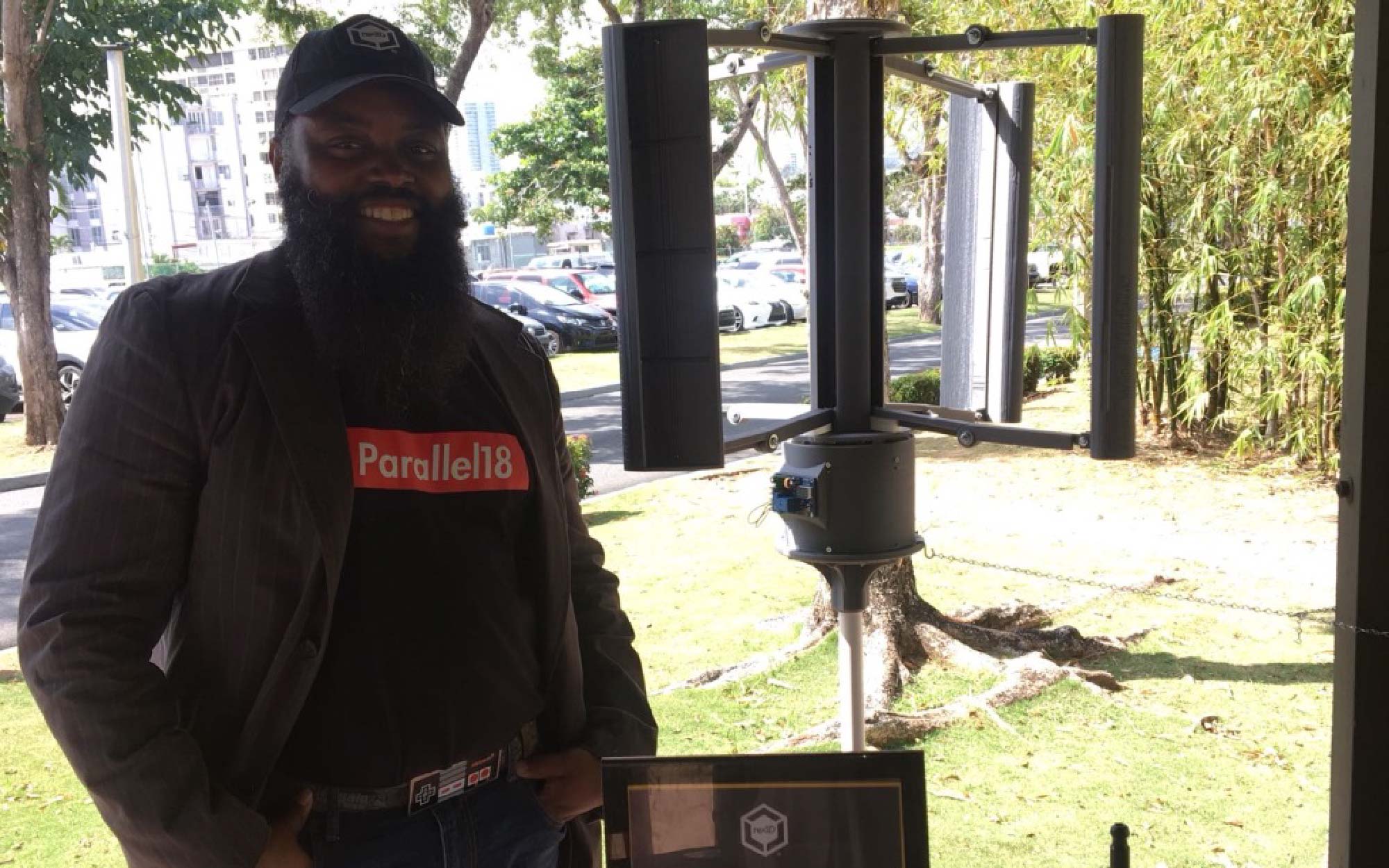
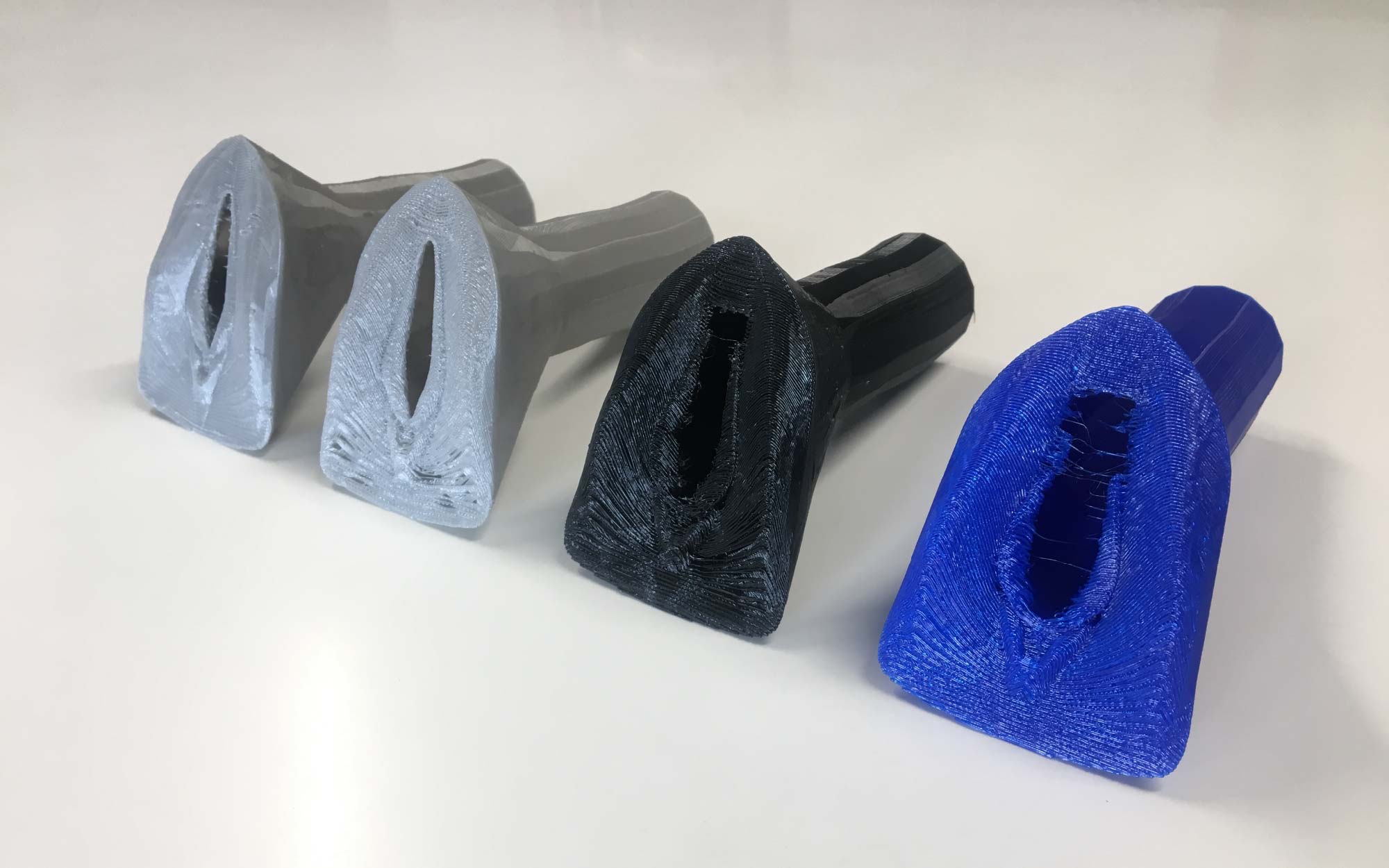
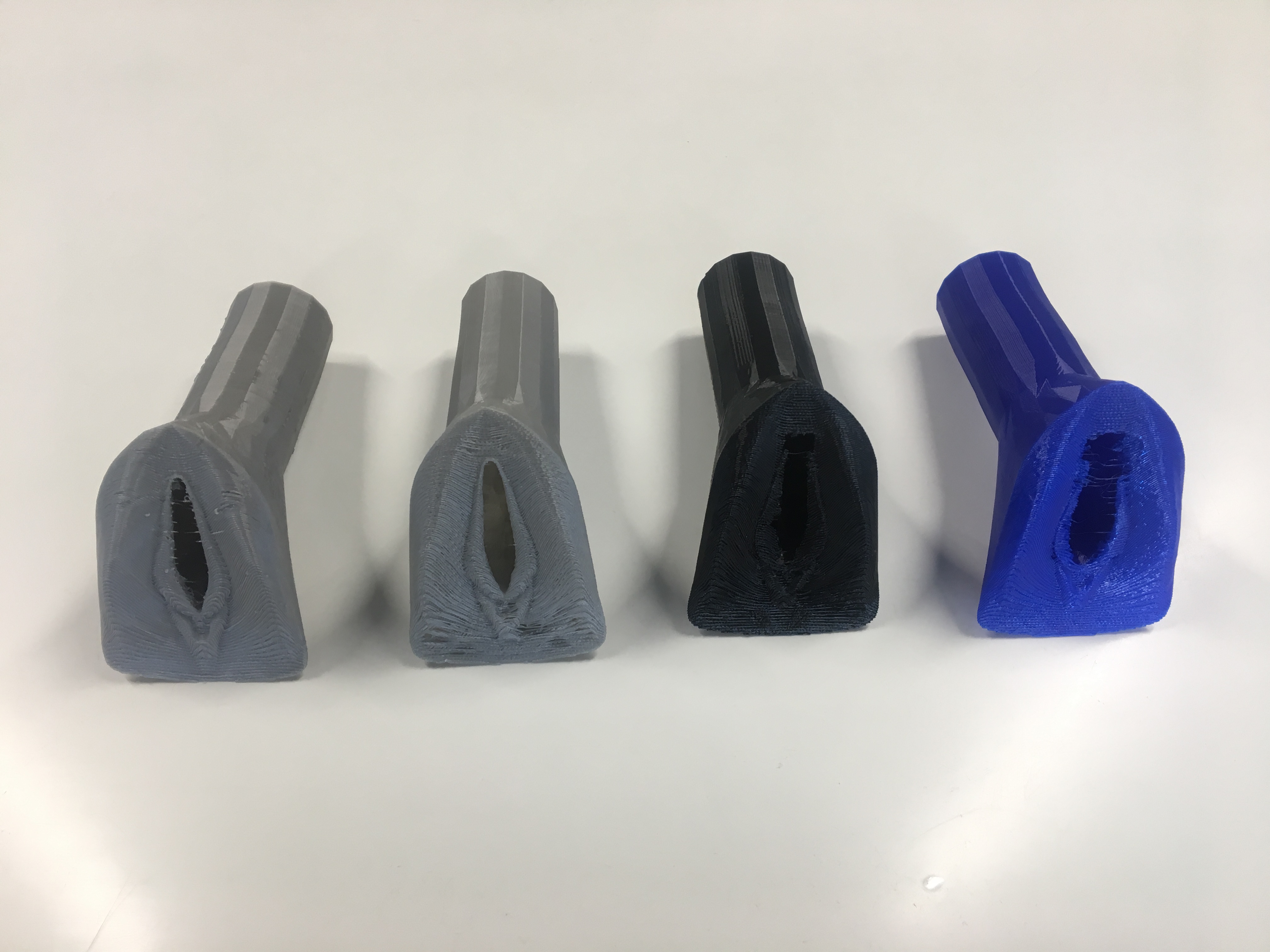
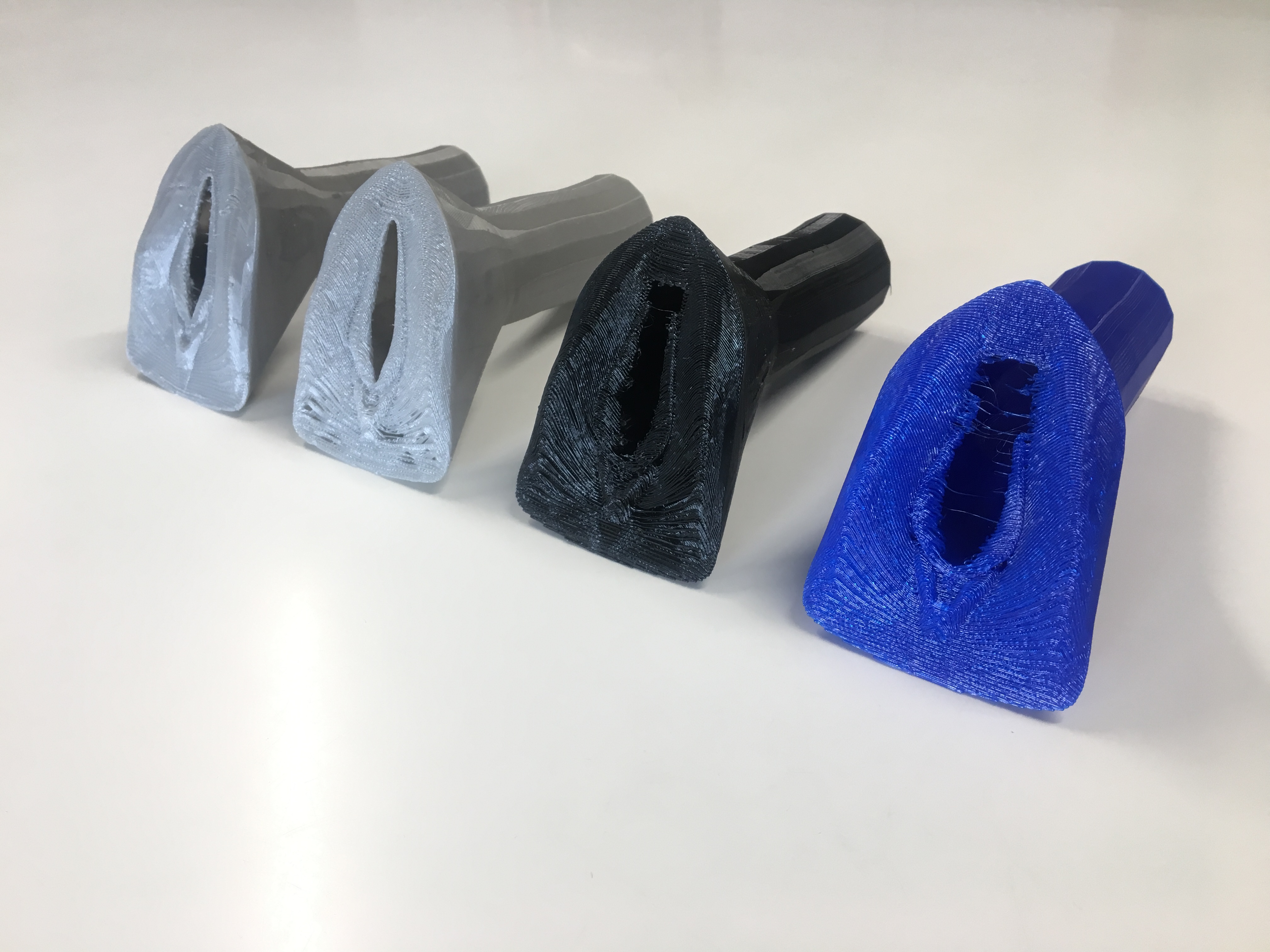
Our team in Puerto Rico decided that Gigabot and 3D printing could get started on making a dent on this problem and set out to 3D print a portable wind turbine with the gusto to charge a cellphone. re:3D hired local maker we met through the Parallel 18 community, a 3D printing enthusiast, founder of MadEra and former Ice Blast HVAC technician, Jean-Yves Auguste Chapiteau, with the knowledge and the know-how to design and 3D print a solution to this challenge.
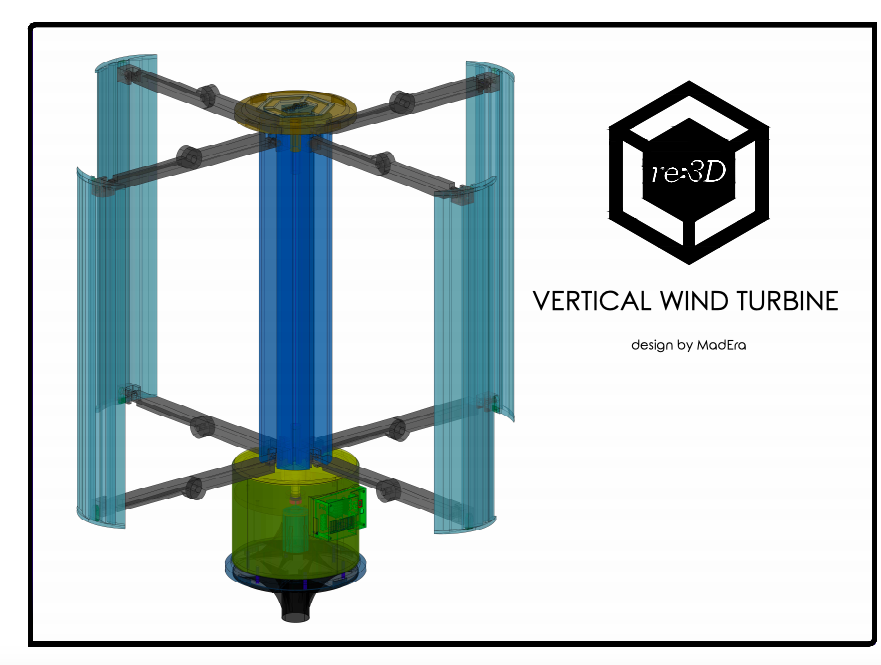
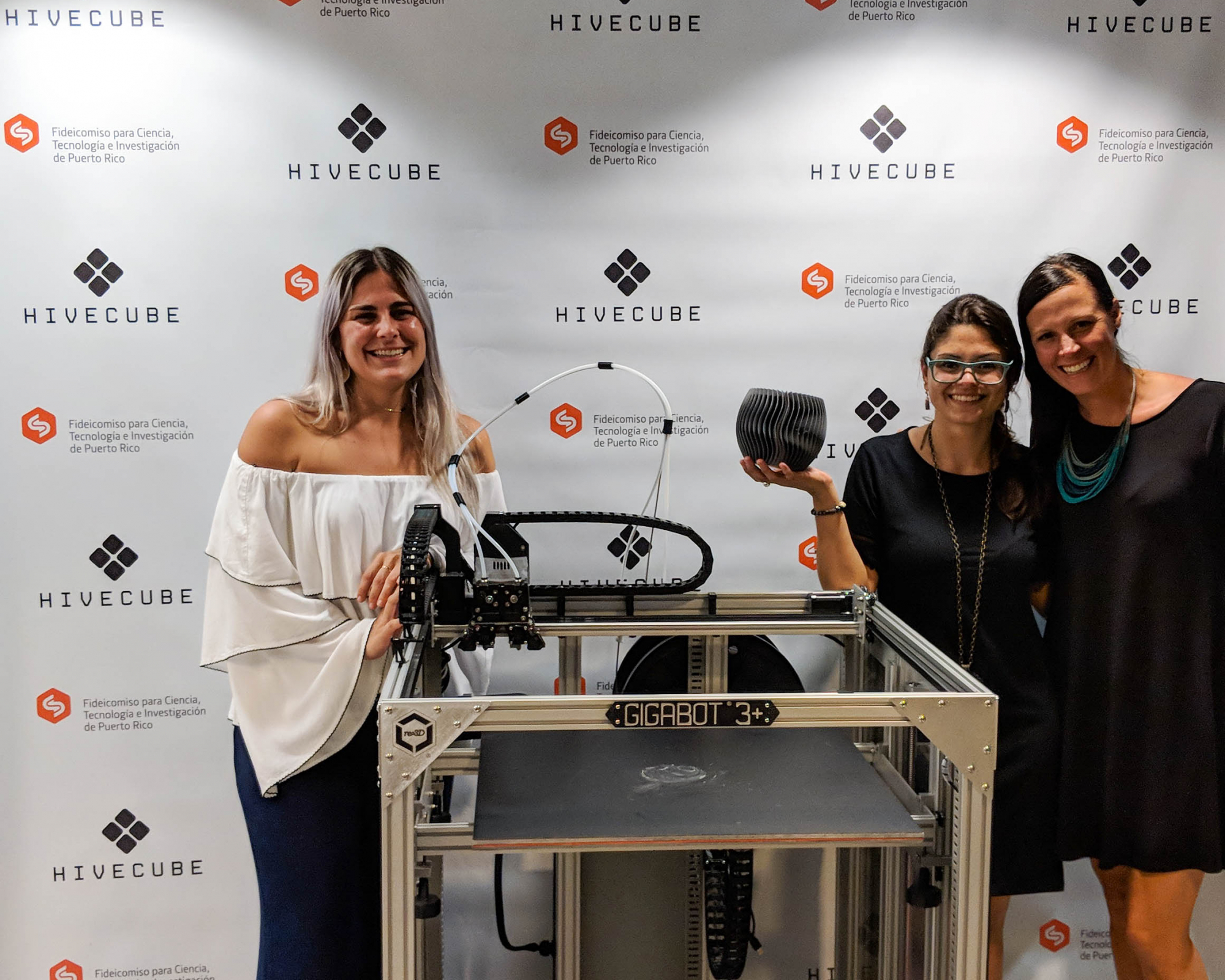
After 5 months, this 3D printable wind turbine takes 200 hours to print with PLA and costs $200-300 including the electrical components, a cost that is 70-80% less than similar sized turbines on the market. Not to mention, it’s designed for easy installation, it doesn’t require maintenance, and its unique vertical axis design optimizes for capturing omnidirectional wind flow and unpredictable wind patterns common to Puerto Rico. It has the power the power up things such as a tablet, cell phone, and small devices.
While still portable, Gigabot’s large format, human-scale 3D printing capabilities expanded this wind turbine’s boundaries of what was possible to be created and empowered the creation of a bigger, more powerful wind turbine.
Compared to his past experience 3D printing with desktop printers, Jean shared it was an impactful difference to print with such bigger parameters which led to bigger opportunities to 3D print not just a bigger solution, but a better solution for a difficult problem. But as Jean says, “There’s no difficult job if you have the right tools”.
Cat George
Blog Post Author