Support
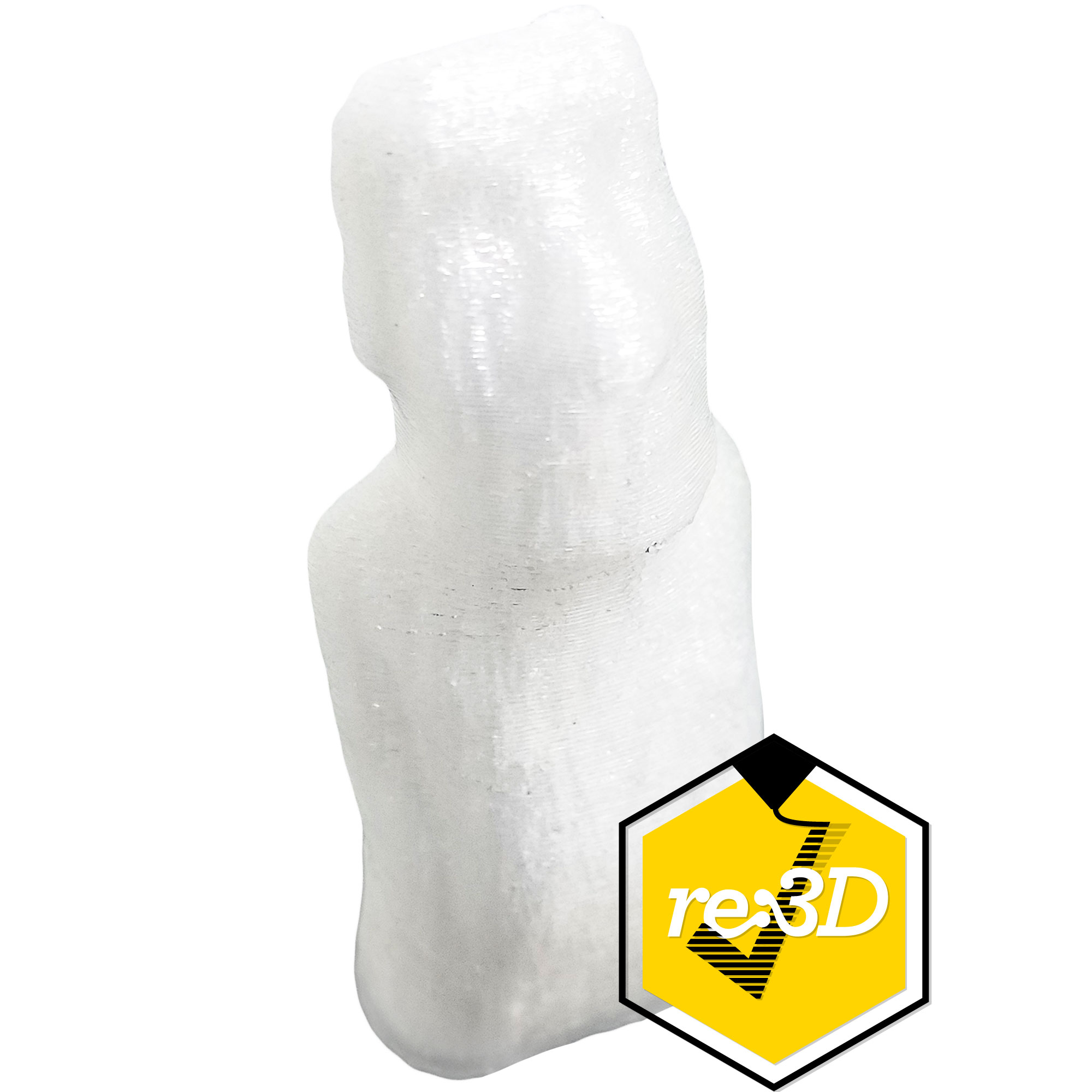
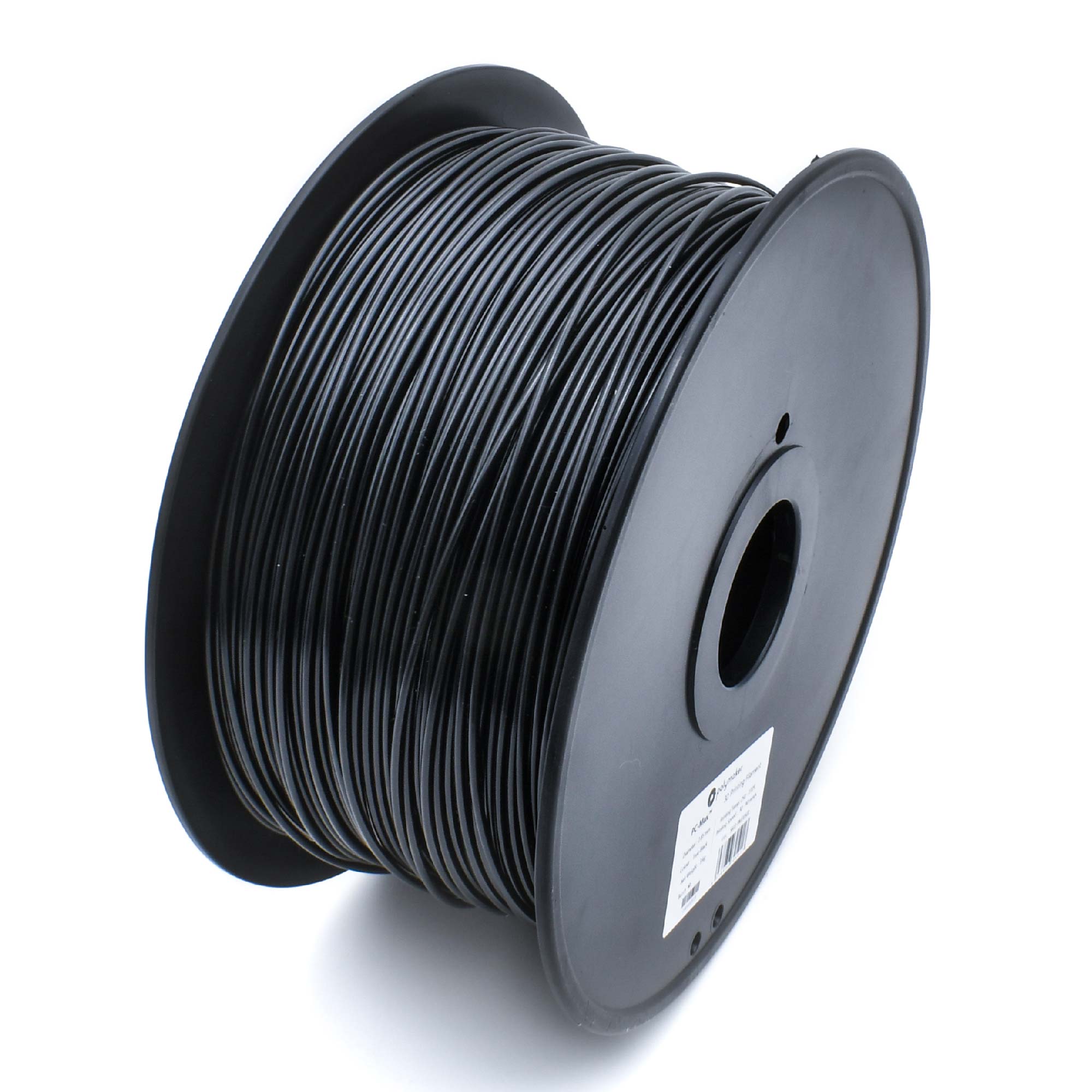
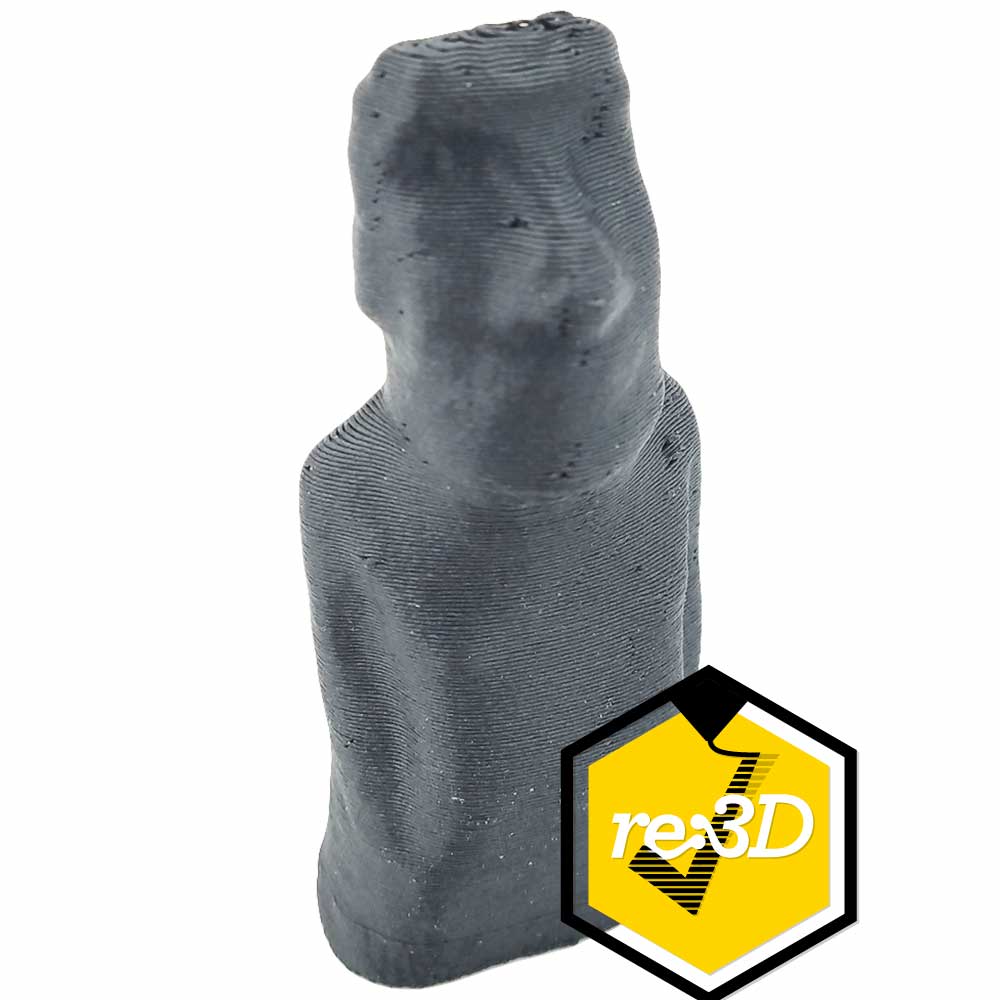
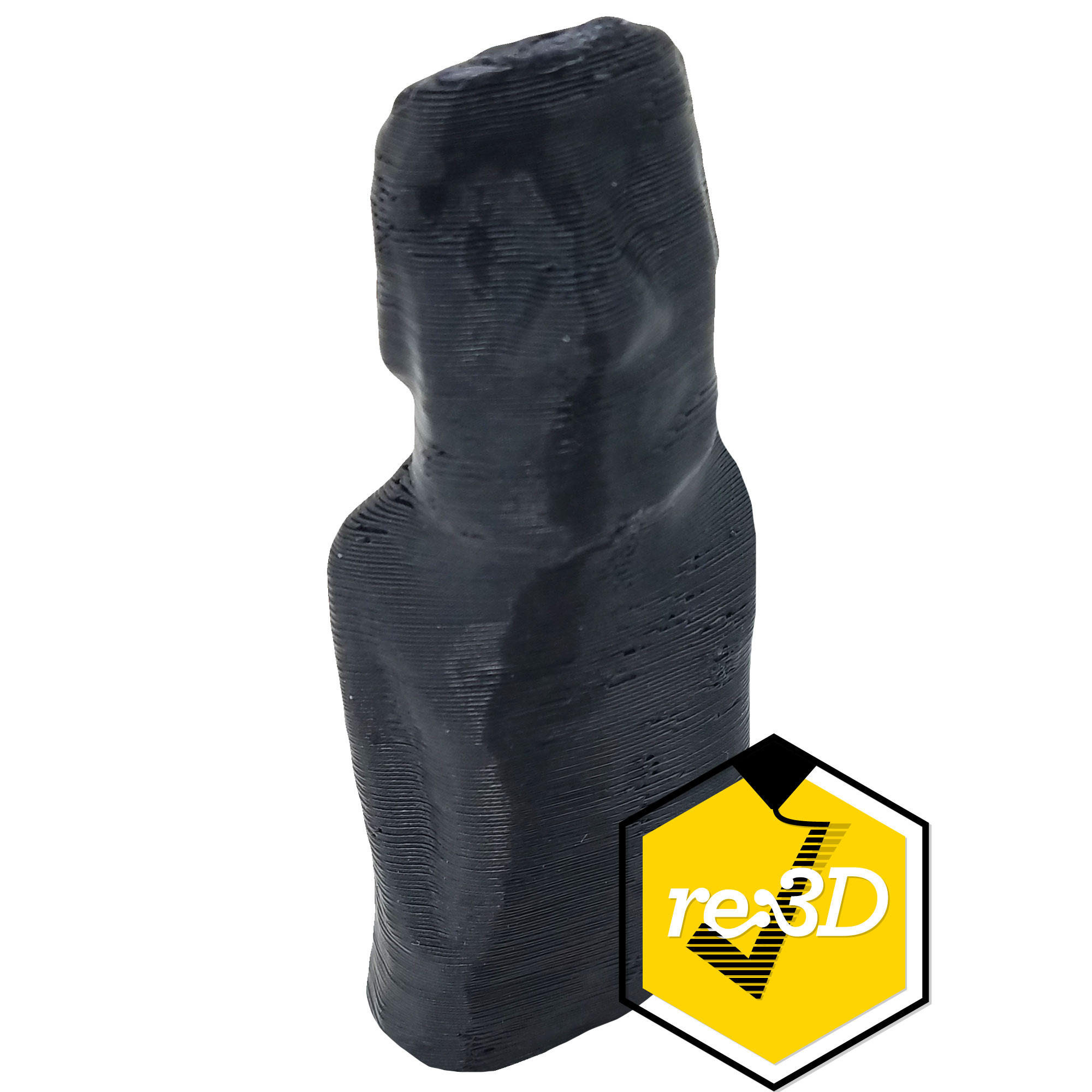
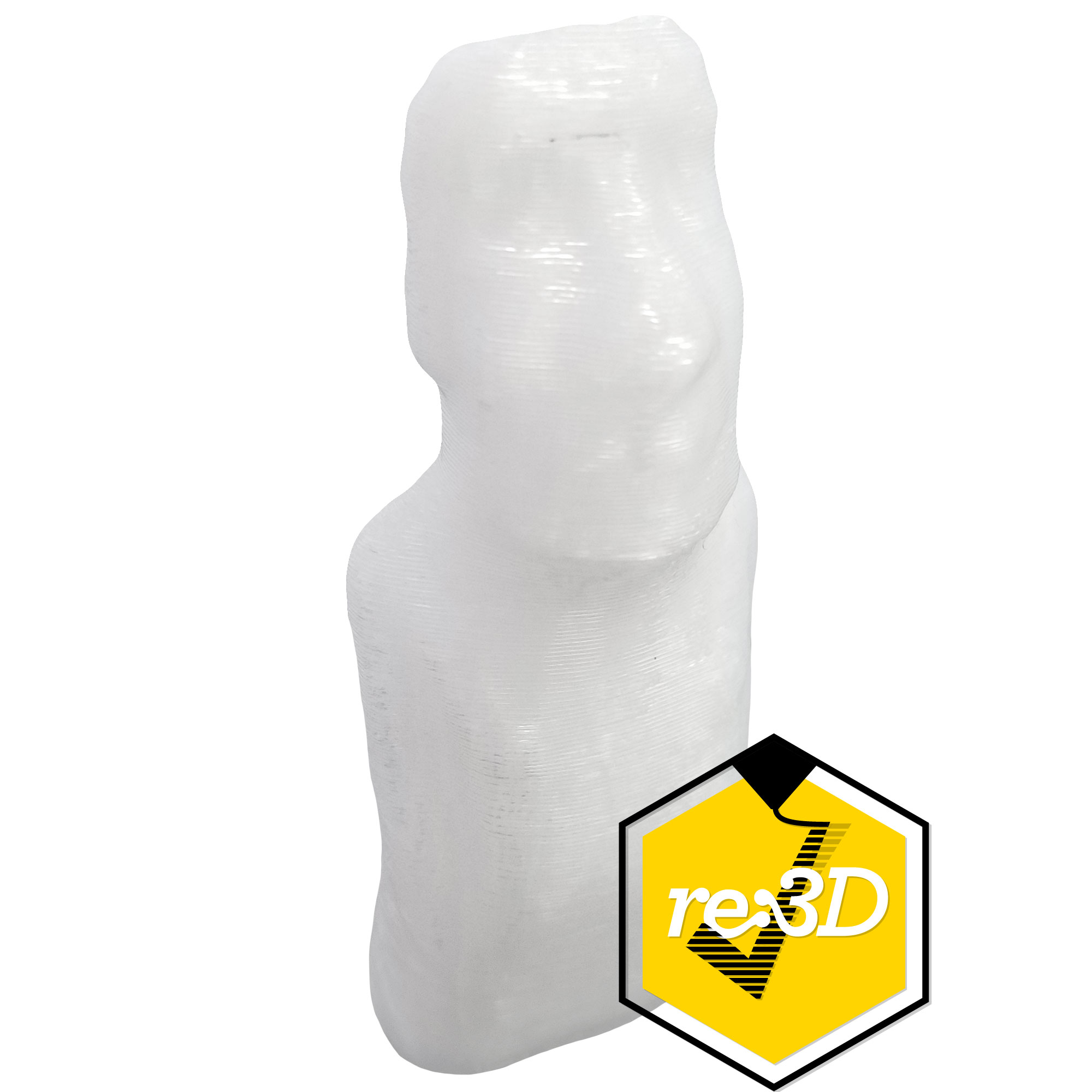
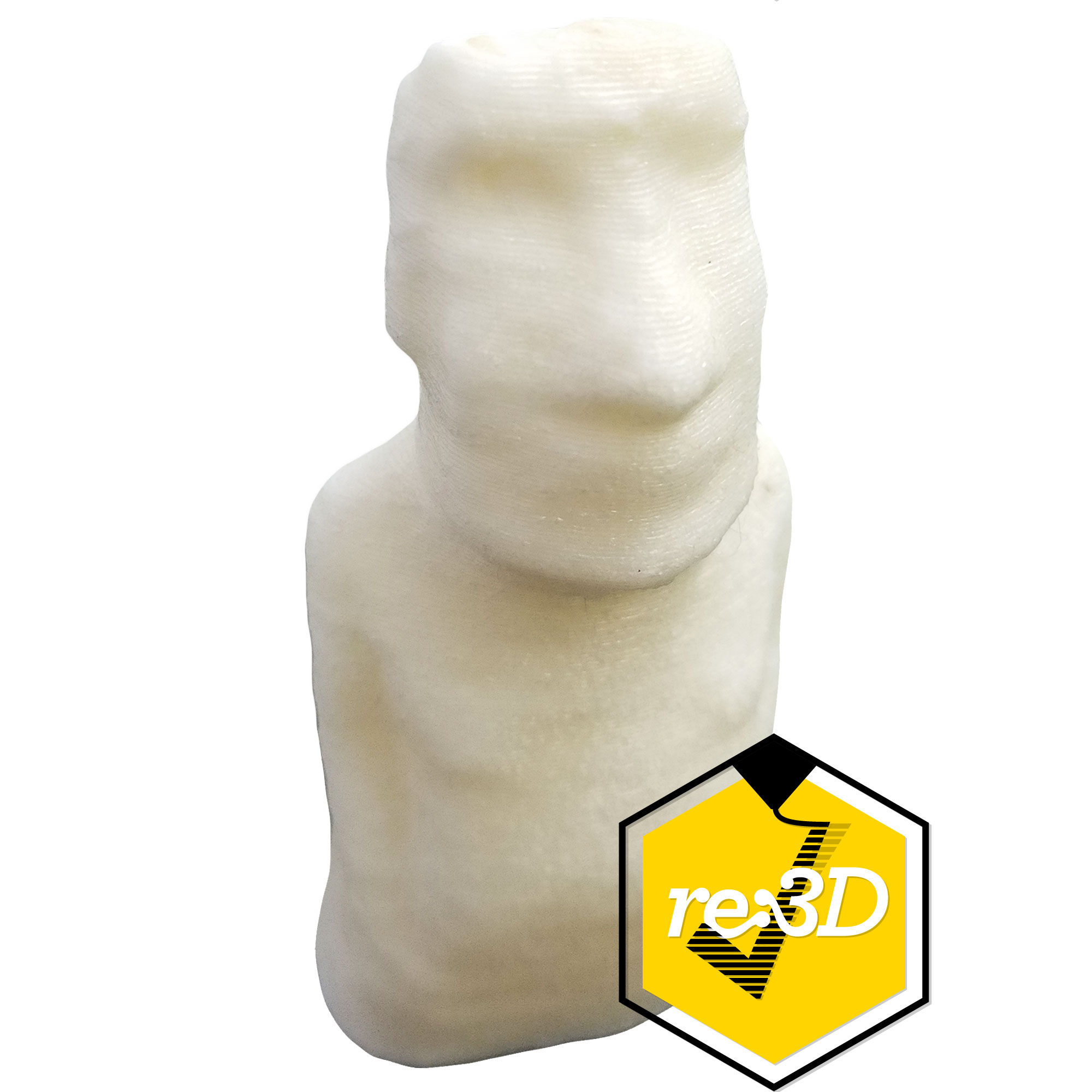
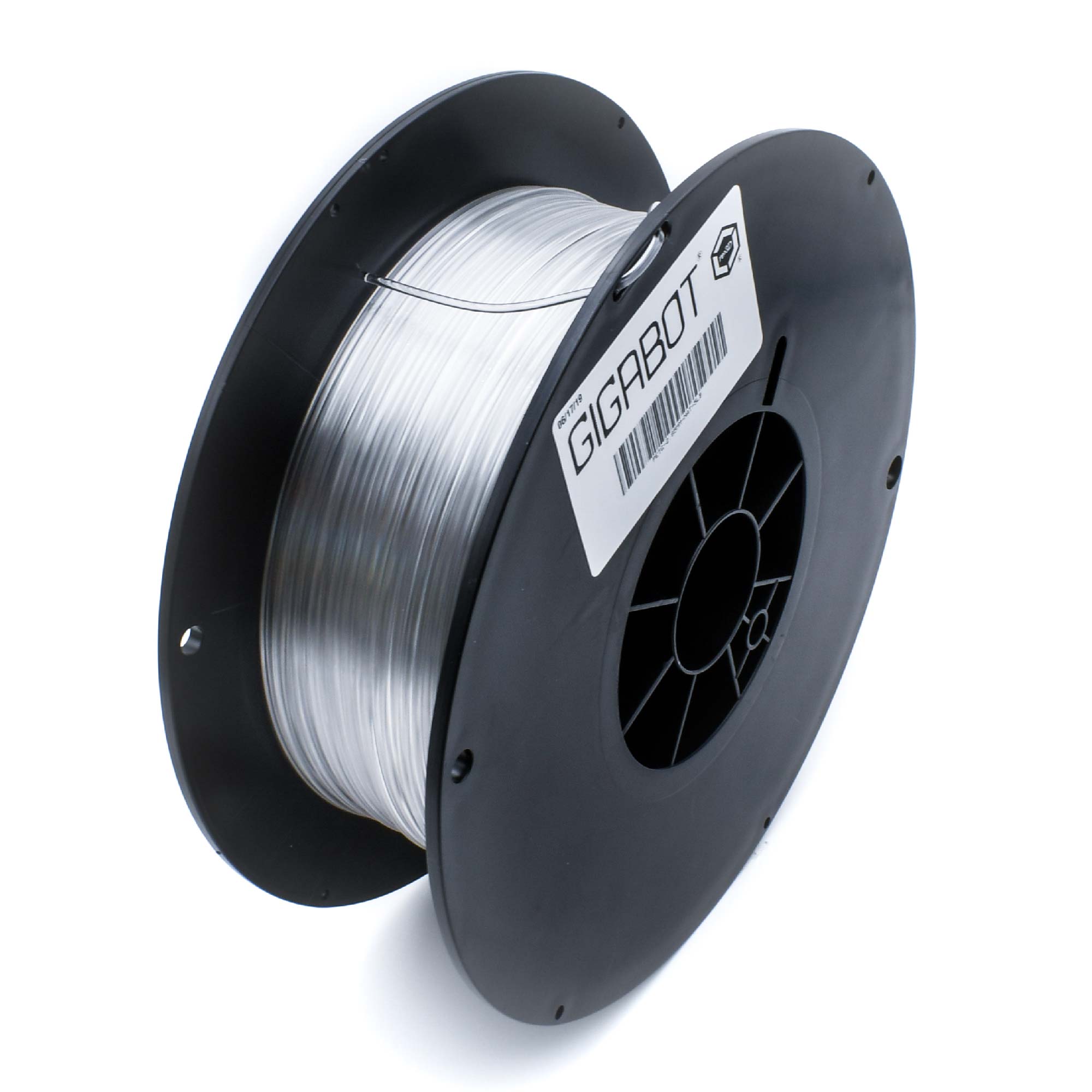
Support material is a class of materials dedicated to serving as easy to remove support. Supports are required on a lot of complex parts, and depending on the geometry they may be difficult to remove. Support material is designed to be easy to remove, and this is often achieved in two different ways. Some support materials are made of PVA, which is often seen in glue. PVA support materials are water soluble, so PVA supports are removed by submerging a part in water. Other support materials are designed to bond with a specific filament. This helps the support material bond to the part, but also remain easy to remove. If you have a complex part that needs intricate support, consider using a dedicated support material in a dual extrusion setup.
Support material has primarily one application, acting as support! The unique properties of PVA support makes it useful beyond just being support. Sometimes, a part may need to dissolve upon contact with water. PVA support is able to meet this unique application.
- Support Material
- Water Soluble Parts

Density
1.22 - 1.37 g/cm3
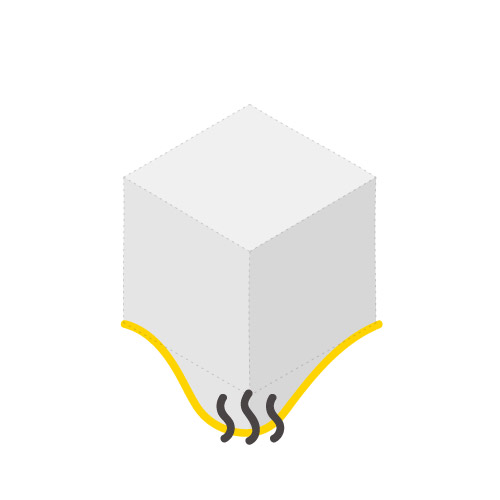
Melt Index
3 - 7.8 g/10 min
Due to the wide variety in resins and chemical makeups of support material, there is no one range of settings used for support. Furthermore, printer settings may vary depending on what material you are supporting. It is best to consult the technical data sheets for your specific support material.
The nature of water-soluble support material makes it difficult to recycle or reuse. The unique resins used for many non-soluble support materials means it’s not recycled commercially. This leads support material to often not be recycled or reused. Regrinding and reusing non-soluble support materials may be possible in pellet printers such as Gigabot X.
- Warmer water makes PVA support dissolve faster but be sure your part can handle the water temperature!
- It’s important to keep dissolvable support material dry when in storage or when printing. Support material that isn’t dried will string much more than dried material.
- Be sure that the support material you choose adheres well to the material you’re trying to print. Some support materials do not adhere as well to other materials!