Antonio Ramos takes a deep breath. “It was really depressing.”
A native Puerto Rican, he was living in San Juan when Hurricane Maria hit. He described the sentiment on the island when the storm was forecasted: Irma had just passed by with little effect, and the general feeling was that Maria would also spare them. The island is used to storms, he explains, and they usually bounced back after big ones in a couple weeks.
But this one turned out to be different.
He remembers seeing the radar images of the vastness of the tempest bearing down on them, their island dwarfed next to it. The dire situation quickly became apparent. Antonio recalls his reaction: “Okay, we’re screwed.”
It wasn’t just Antonio that had to weather the storm – he had a company to tend to as well.
From Capstone Project to Company
Antonio and his cofounder, Alan Lopez, started Parknet when they were still engineering students in university. They used the idea for their Capstone Project, building a controller that could connect to the Internet using Wi-Fi or SIM cards and control a boom barrier or electromagnetic gate – “really anything that could be activated,” Antonio explains.
They approached a local company with their idea, proposing to them that they could reprogram their controller in real time.
“They actually challenged us,” recounts Antonio. “They told us, ‘Hey, that can’t be done.’” The company said the only way to reprogram it was to go into a computer, use their software, and reprogram the whole controller.
Antonio didn’t balk. “I told them, ‘No, we can actually hack your controller.’” The company didn’t budge.
“So, it was a challenge,” says Antonio. “And challenge accepted. Something that we’ve learned is that you never challenge an engineer and say that they can’t do something, because they will do it.”
Six months later, Antonio and Alan demoed for the company their “unhackable” controller working as they had originally pitched. Parknet was born.

Maria's Arrival
Parknet makes cloud-based controlled access systems which provide facility administrators the ability to control access points – think entry doors or parking gates – in real-time, through the use of a web-based app accessible from any device with an internet connection.
Antonio and Alan explored different routes for how to market their system in Puerto Rico.
“At first, we wanted to use it for a parking lot payment system. But we found a bit of resistance here from the parking administrators,” Alan explains. They shifted their focus to gated communities and apartment complexes.
They joined the Generation Four cohort of Puerto Rican incubator program Parallel18 in August. And then, in September, Maria arrived.
“After the hurricane, we had no cell phone communication, we had no Internet, no power. It was really depressing,” Antonio recounts. “Our business needs Internet. It’s an Internet of Things device, so it needs Internet to operate and it needs power. So we were kind of stuck there.”
They pivoted yet again, strategizing how to stay afloat and retain their employees.
“We had to survive,” Antonio says. “The sales cycle for gated communities and apartment complexes can be from four to six months. It takes a lot of time and a lot of meetings and convincing.” But they found that with commercial spaces, the process was faster. “We started selling to co-working places and offices.” One such customer is Parallel18 itself.

Antonio stopped paying himself in order to keep his team on payroll. “We were in survival mode,” he explains. He began working in generator repairs, a service in high demand on the island following Maria.
They weathered the monster storm and its lingering aftermath, and several months later the company was back on its feet. As Parknet started demanding more from Antonio, he wrapped up his generator repair work and went back to it full time.
3D Printing Before Moving to Manufacturing
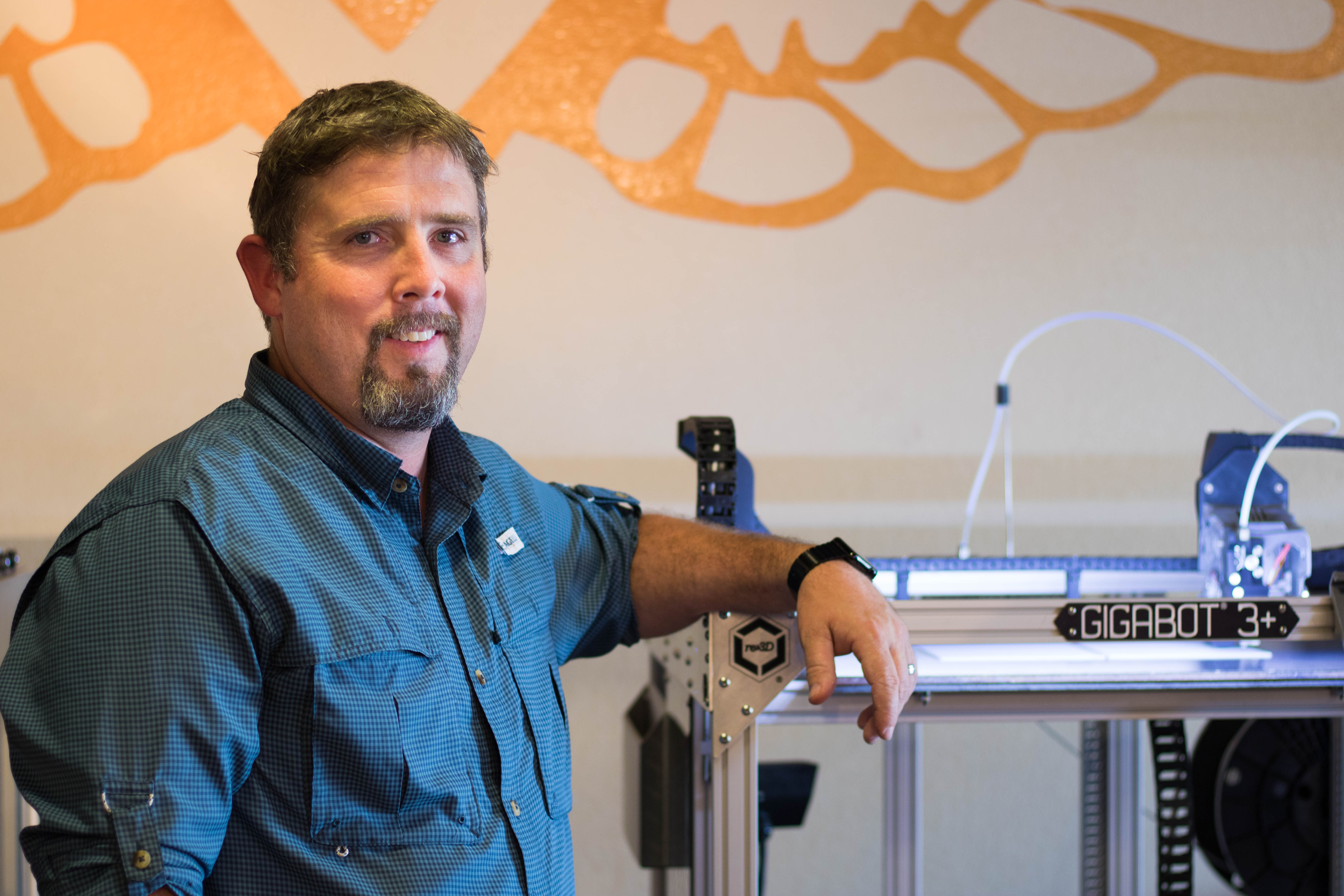
In the Parallel18 program, Parknet crossed paths with re:3D.
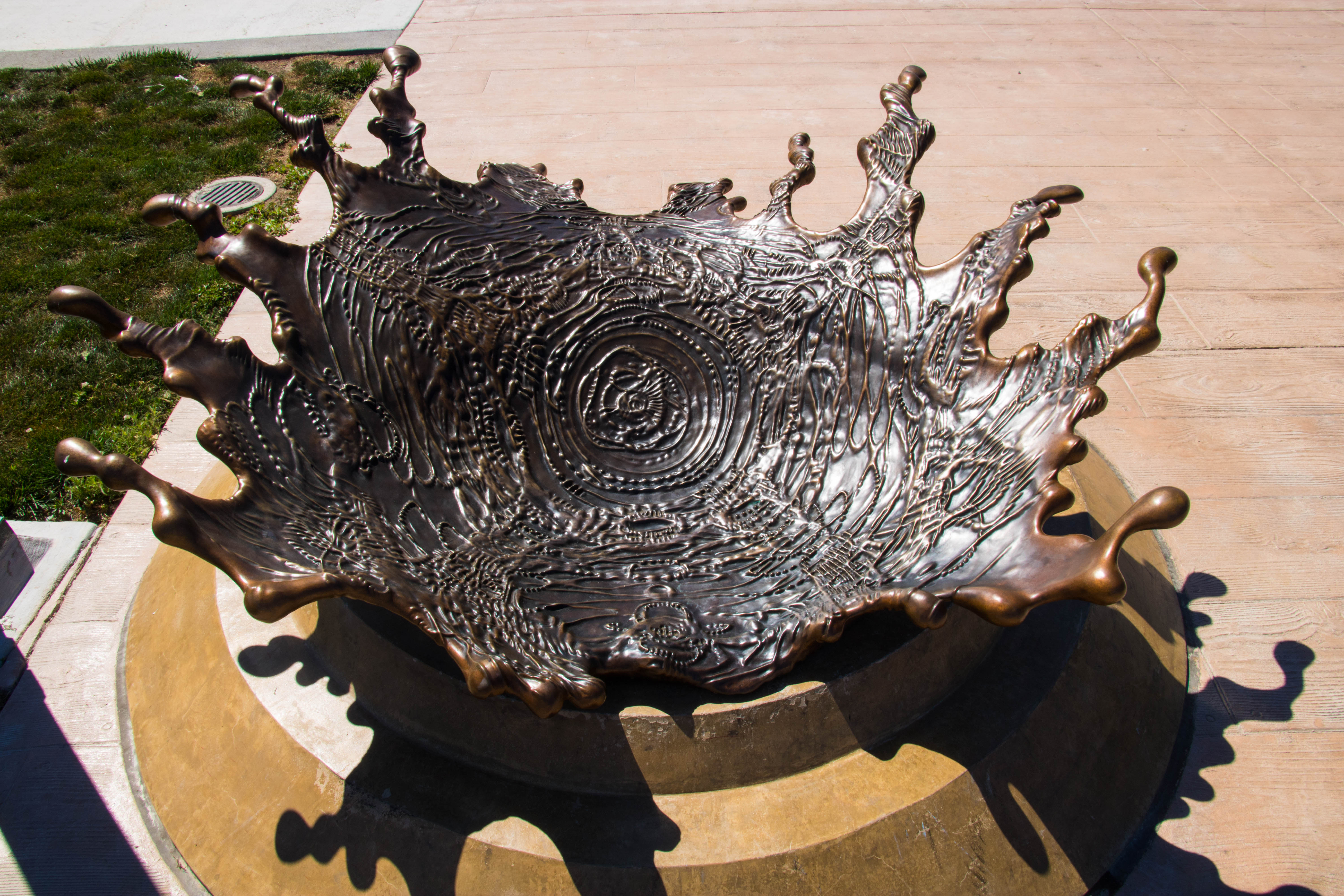
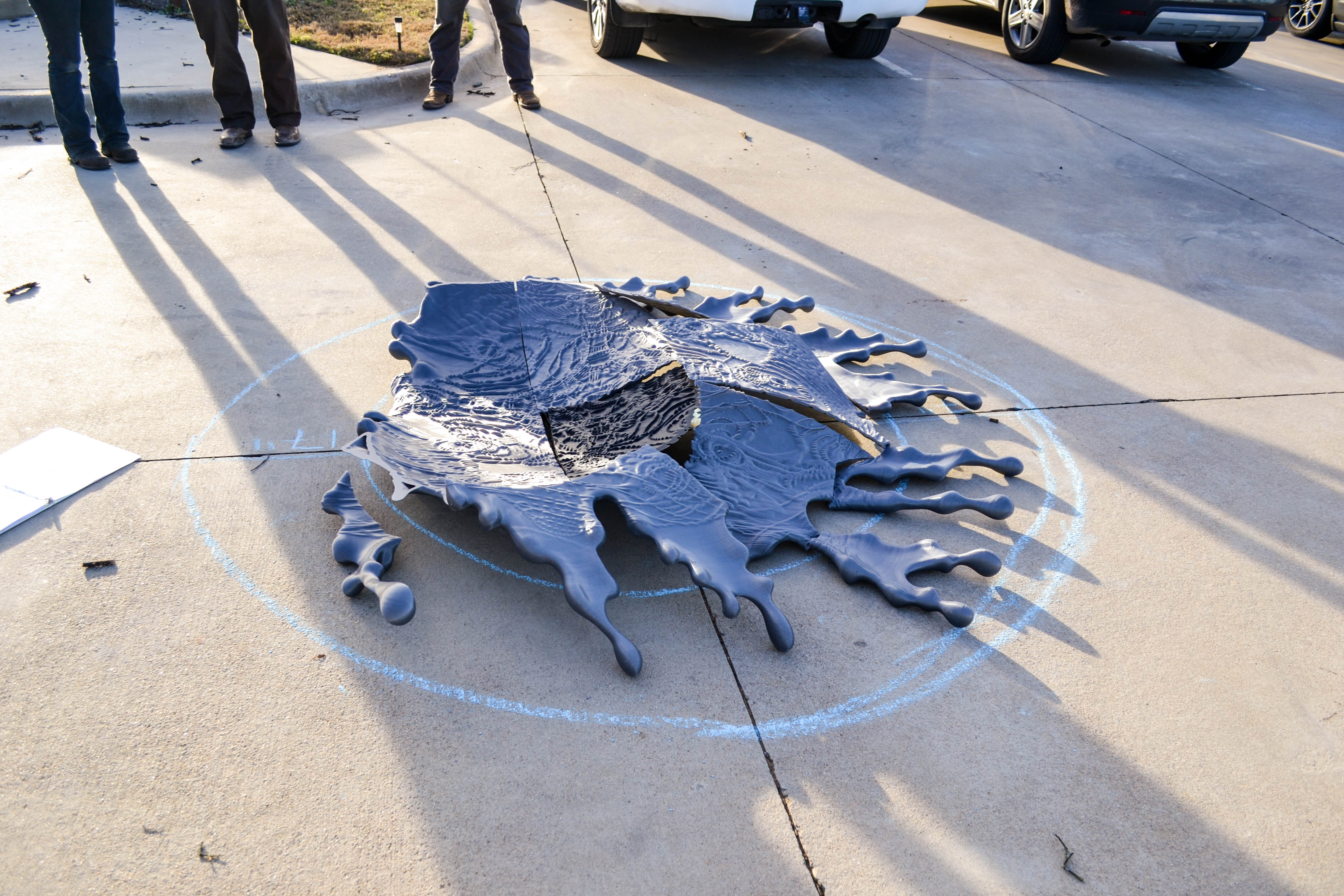
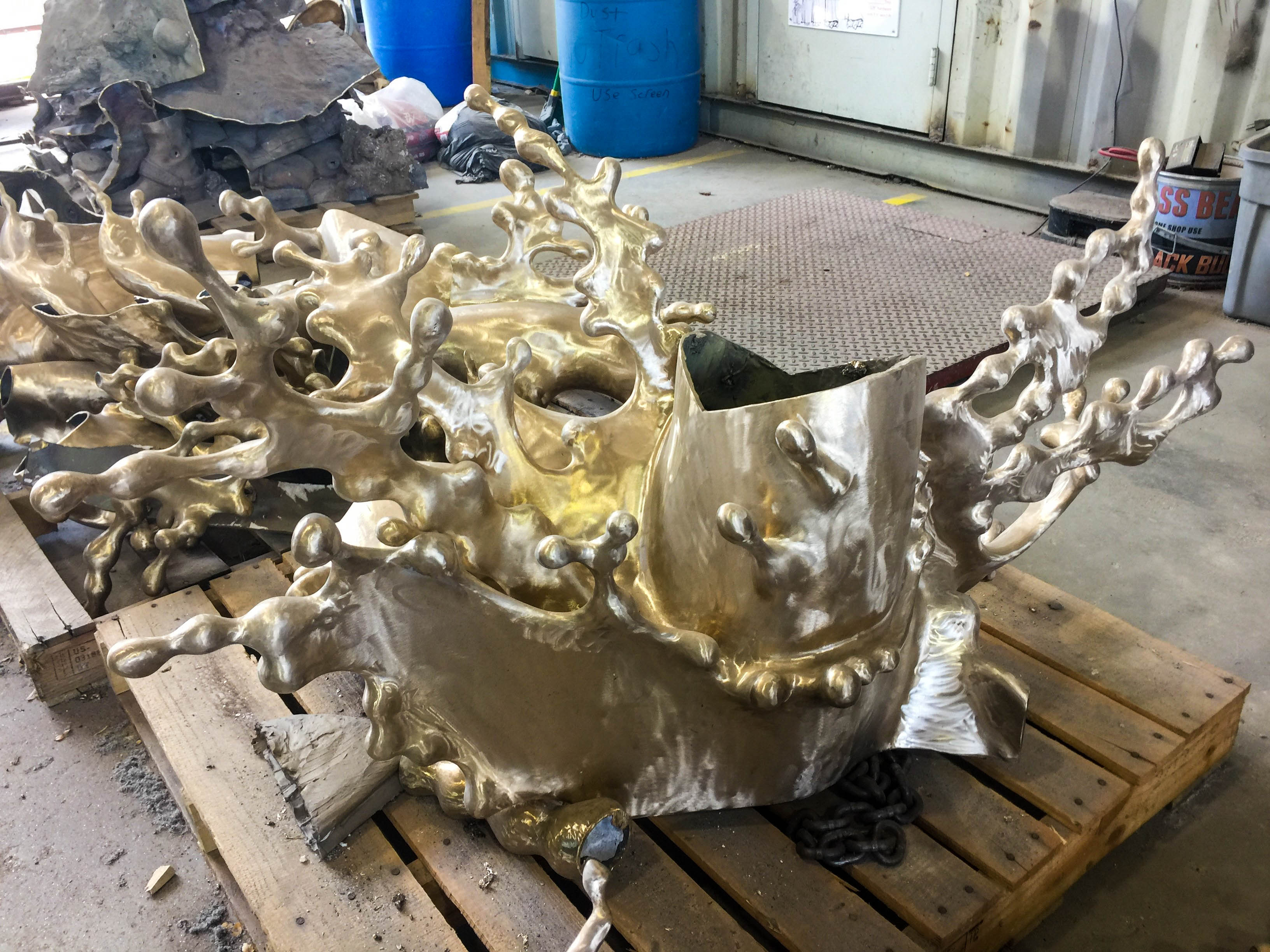
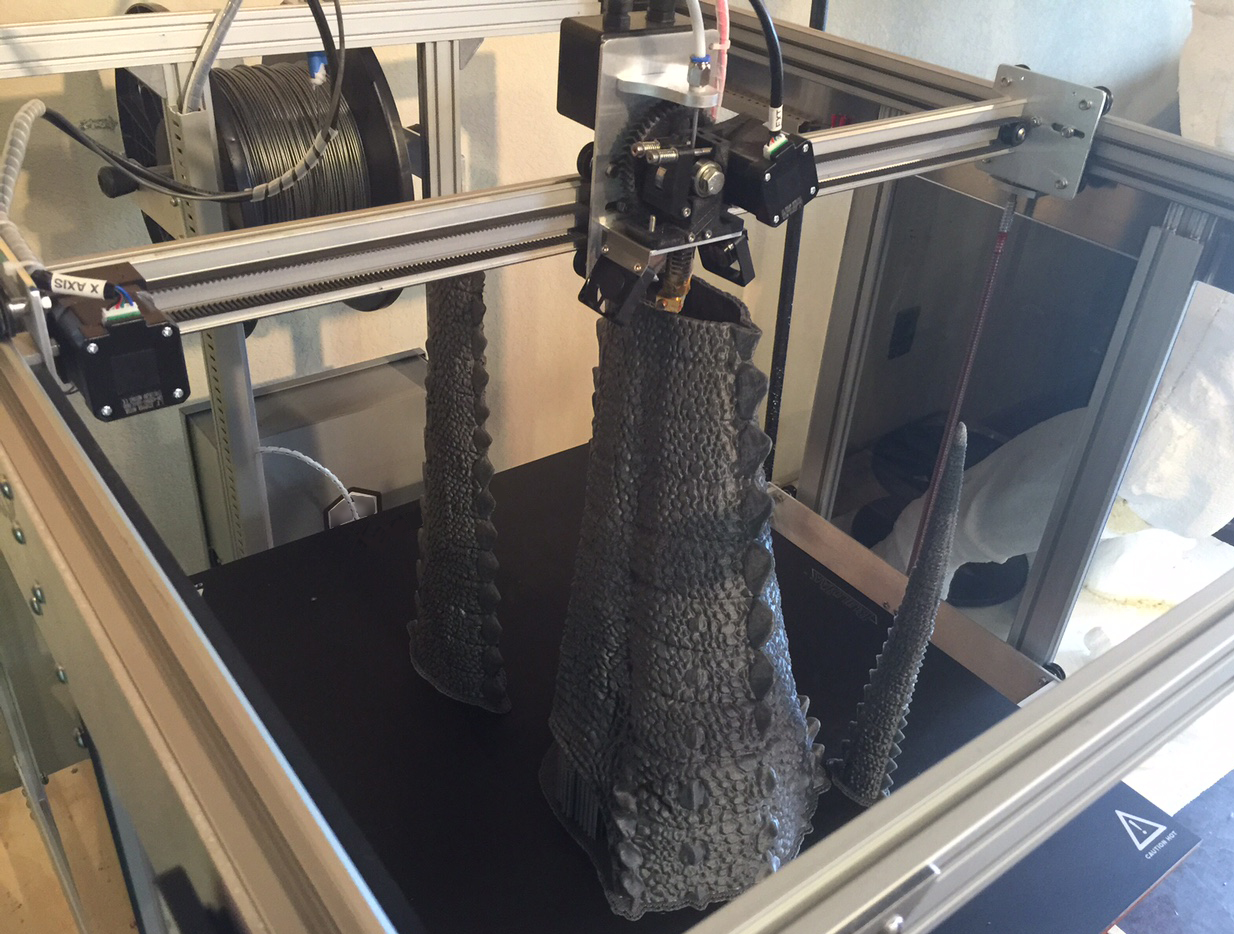
They began using Gigabot to 3D print enclosures for their printed circuit boards, or PCBs. “We can build a box in like, two hours, and we can test it before we send it to the manufacturer,” Antonio explains. “The manufacturer had a minimum of 10 boxes, and if it didn’t work correctly, we were going to waste 10 boxes.”
Once they finalized the enclosure design, they moved to a sheet metal forming process, but they continued to turn back to Gigabot for custom requests. “One of the advantages is that we can offer a customer a custom design,” Antonio says. “If they want a diamond shaped scanner, we can build it for them. If they want it embedded into a gypsum board, we can also do that.”

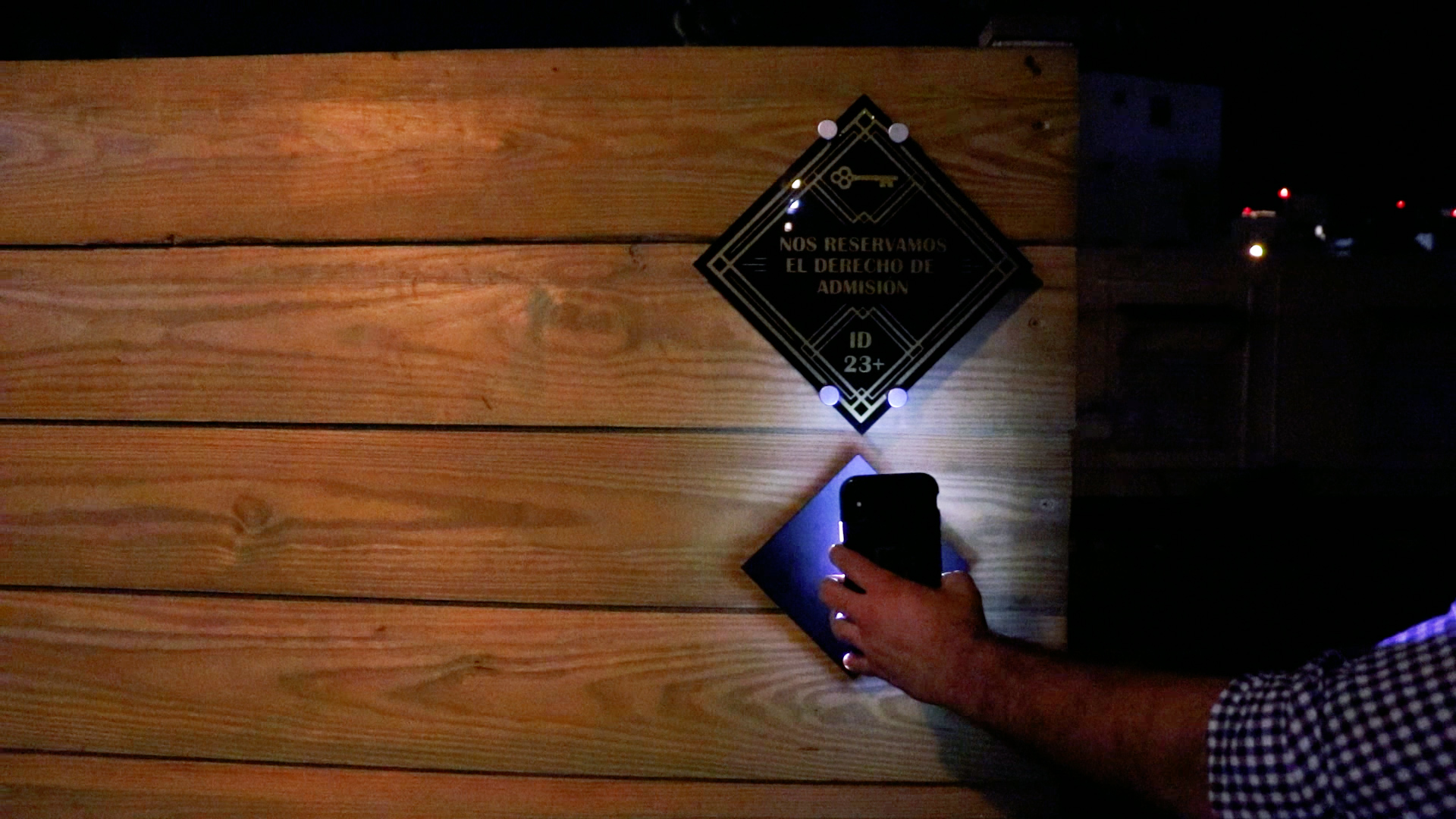
One Parknet customer in San Juan who has requested a diamond-shaped scanner is El Almacén, a speakeasy-style bar tucked away just off the buzzing square of La Placita.
They’re using Parknet’s technology to text message patrons digital keys and grant them entry to the bar with the swipe of a phone. The door unlocks and the e-key-holder descends into an old-timey themed lounge.
It also gives the bar the marketing opportunity to track and quantify their marketing. They can compare how many people the text message key was sent to and how many people used it, rather than their old method, which was a post on their Facebook page with the password for the night. There is also the location-based aspect of it – if a patron gets within a certain radius of the bar, their phone will remind them that they have a key to the nearby locale.

Moving Forward Post-Maria
It’s just past the one year anniversary of Hurricane Maria’s landfall.
Puerto Rico has recovered fairly well given the incredible destruction of the storm. The land itself looks lush and green, and the people I spoke with are propelled by a resilient spirit and a desire to rebuild and strengthen their island for the future.
Antonio is one of those very people. Parknet came out the other side of Maria arguably a stronger company, with more applications and a wider customer base than he and Alan had originally imagined. It’s been a big cycle for them that has taken them through multiple major pivots in the company’s lifespan.
After the trials of Maria, Parknet is now focused back on gated communities and apartment complexes and is ready to tackle their original vision of parking lots.
Learn more about Parknet: https://www.linkedin.com/company/parknet.pr/about/
Learn more about Parallel18: https://www.parallel18.com/

Morgan Hamel
Blog Post Author