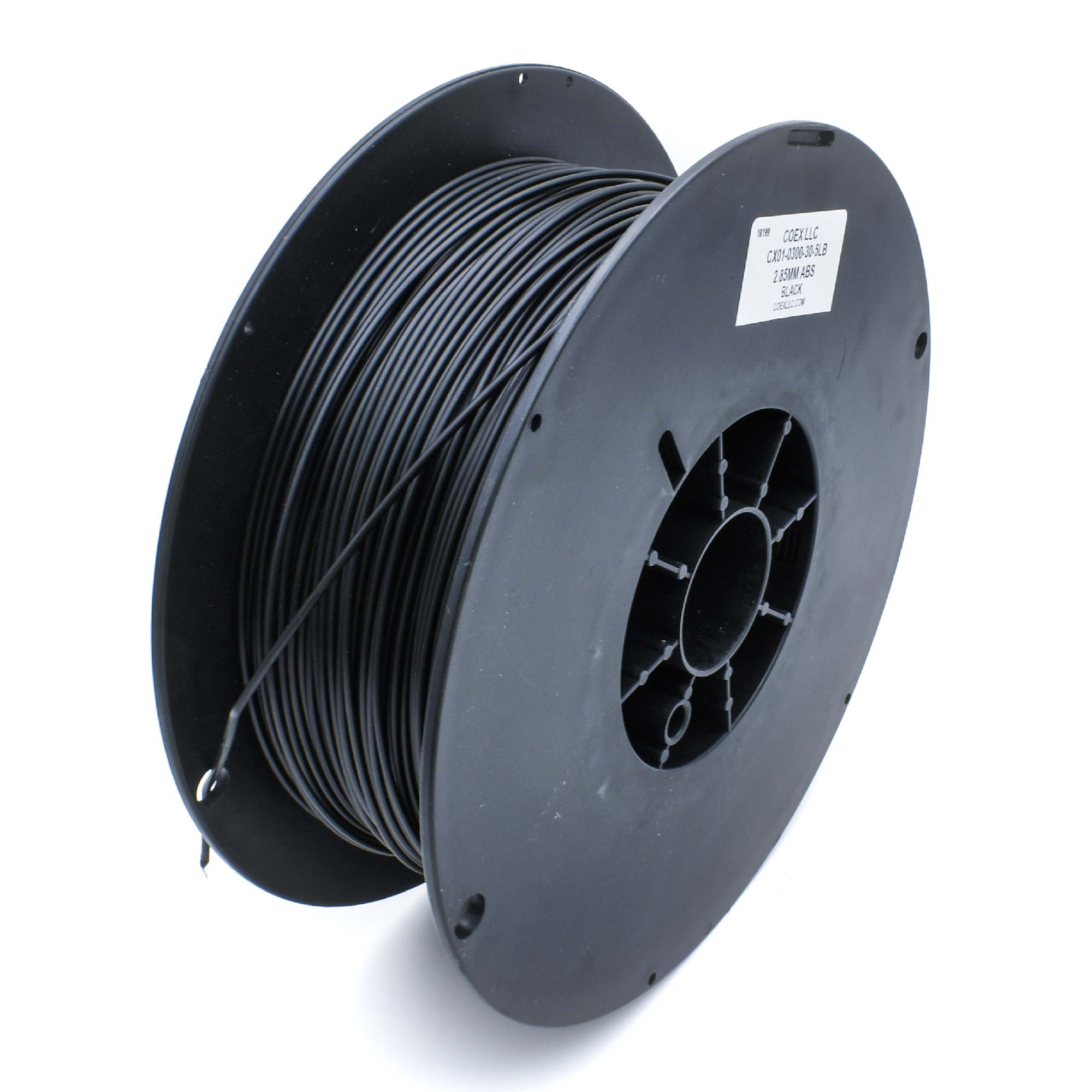
ABS
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is another common 3D printing material with popularity that rivals PLA. ABS’s structure contains a long chain on butadiene that crosses with shorter chains of acrylonitrile and styrene. The proportions of each monomer in ABS can vary. ABS is resistant to heat and to impact damage making it a durable material suitable for the outdoors. Its mechanical and thermal properties also give parts a cleaner finish compared to PLA. Due to its chemical nature, printing with ABS usually requires a raft in order to guarantee bed adhesion. This makes it a suitable material for those who have some experience with 3D printing already.
ABS’s durability and temperature resistance allow it to endure life outside. This makes it a good material for enclosures outside. ABS also serves as a good material for custom pipes that may operate outside. ABS’s durability and price point enable it to serve as a suitable material for handles on devices such as power tools. ABS can also replace automotive trim and endure usage on a car. ABS is also the material used in LEGOs. For those wanting to replicate or create new LEGOs, ABS is a perfect material.
- Outdoor Enclosures
- Handles
- Custom LEGOs
- Automotive Trim
- Piping
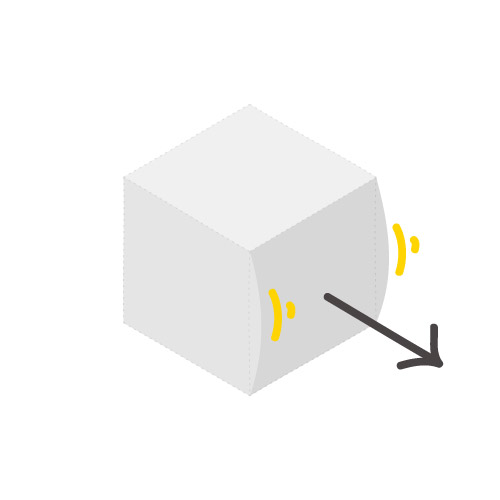
Young's Modulus
2,174 MPa
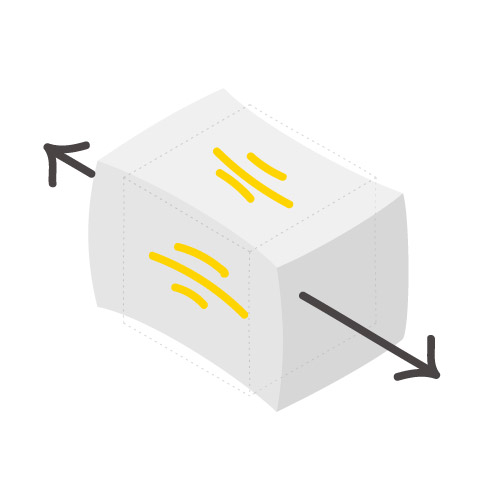
Tensile Elongation
2.7 %
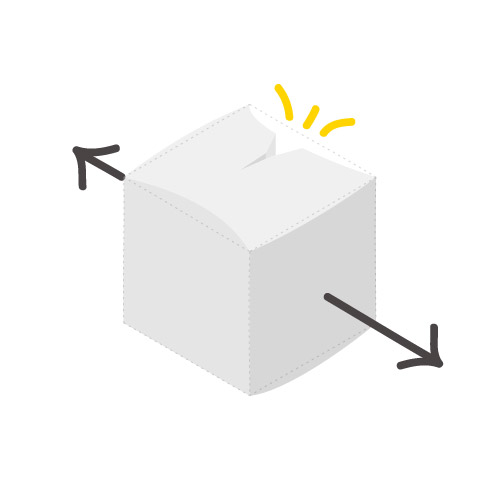
Ultimate Tensile Strength
33.3 Mpa
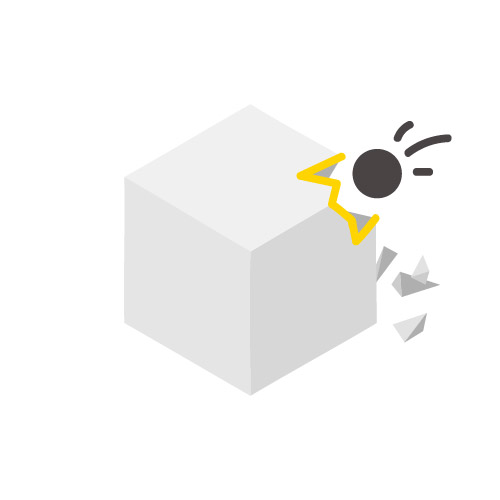
Charpy Impact Strength
12.6 J/m2
Shrinkage Rate below 0.5%
-

Glass Transition Temperature
101 ºC
Vicat Softening Temperature
104 ºC

Decomposition Temperature
> 380 ºC
Extruder Temperature
235 ºC

Heated Bed Temperature
105 ºC
Bed Adhesion
Clean Bed
Enclosure
Required
Fans
Off
Printing Speed
3,600 mm/min
ABS is an easily recyclable and reusable filament. It is easy to regrind and reuse in pellet extruder printers such as GBX. It is also easy to mix and reuse with virgin ABS once sorted. Since ABS is a durable material, it can take the place of many single-use plastics as well.








